Abstr:Premixed Methane-Air Swirl Burner (TECFLAM): Difference between revisions
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
''Contributors: | ''Contributors: Guido Kuenne (EKT), Andreas Dreizler (RSM), Johannes Janicka (EKT)'' <br> | ||
EKT: Institute of Energy and Power Plant Technology, Darmstadt University of Technology <br> | ''EKT: Institute of Energy and Power Plant Technology, Darmstadt University of Technology'' <br> | ||
RSM: Institute Reactive Flows and Diagnostics, Center of Smart Interfaces, Darmstadt University of Technology | ''RSM: Institute Reactive Flows and Diagnostics, Center of Smart Interfaces, Darmstadt University of Technology'' | ||
{{AC|front=AC 2-08|description=Description_AC2-08|testdata=Test Data_AC2-08|cfdsimulations=CFD Simulations_AC2-08|evaluation=Evaluation_AC2-08|qualityreview=Quality Review_AC2-08|bestpractice=Best Practice Advice_AC2-08|relatedUFRs=Related UFRs_AC2-08}} | {{AC|front=AC 2-08|description=Description_AC2-08|testdata=Test Data_AC2-08|cfdsimulations=CFD Simulations_AC2-08|evaluation=Evaluation_AC2-08|qualityreview=Quality Review_AC2-08|bestpractice=Best Practice Advice_AC2-08|relatedUFRs=Related UFRs_AC2-08}} | ||
Revision as of 15:09, 11 January 2011
Application Area 2: Combustion
Application Challenge AC2-08
Abstract
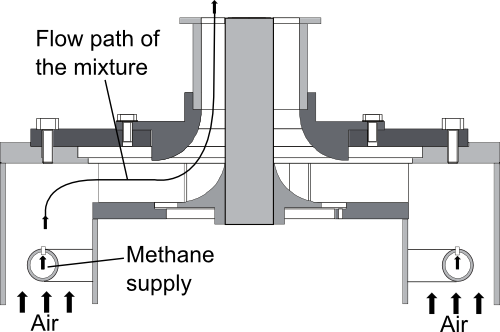
The TECFLAM configuration is a lean premixed methane-air burner with a high swirl intensity where the flame is stabilized by the recirculation of hot products. It is designed to investigate essential features found in industrial lean premixed combustors. An extensive set of measurements obtained by advanced laser-diagnostics exists to:
- Give insight into the underlying physics to gain a deeper understanding of the relevant phenomena
- Build a database well suited for CFD validation
Validation data is available for the reacting and non-reacting cases using the same velocity boundary conditions to allow for a separate assessment of the applied turbulence model and combustion model. A total of four cases are considered in this AC consisting of a 30 kW and 150 kW flame and their corresponding isothermal cases.
Contributors: Guido Kuenne (EKT), Andreas Dreizler (RSM), Johannes Janicka (EKT)
EKT: Institute of Energy and Power Plant Technology, Darmstadt University of Technology
RSM: Institute Reactive Flows and Diagnostics, Center of Smart Interfaces, Darmstadt University of Technology
© copyright ERCOFTAC 2011