Description AC2-09
SANDIA Flame D
Application Challenge AC2-09 © copyright ERCOFTAC 2024
Introduction
Sandia flame D [1] (shown in Fig.1) is a widely used test case for validation of numerical models of non-premixed combustion. The fuel stream is composed of 25% methane (CH4) and 75% air. The pilot flame is a lean mixture of C2H2, H2, air, CO2 and N2 with the same nominal enthalpy and equilibrium as methane/air at the equivalence ratio 0.77. Partial premixing with air also reduces the flame length and produces a more robust flame than pure CH4 or nitrogen-diluted CH4. Consequently, the flames may be operated at reasonably high Reynolds number with little or no local extinction, even with a modest pilot. The mixing rates are high enough that these flames burn as diffusion flames, with a single reaction zone near the stoichiometric mixture fraction and no indication of significant premixed reaction in the fuel-rich CH4/air mixtures. Flame D (Re=22400) has a small degree of local extinction. It can be assumed that the Flame D operates in a flamelet regime that means there is a scale separation between turbulence length and time scales and the scales characterizing the combustion process. Despite that the Sandia D Flame is not a demanding test case it seems to be worth to study various combustion/turbulence interaction models on this example as a starting point to more complex flame with local extinction and reignition. As an Application Challenge such a flame facilitates to study models of turbulence/chemistry interaction allowing to separate the influence of turbulence and turbulence/chemistry interaction models from the influence of chemical kinetics applied.
Focusing on the LES approach to the Sandia Flame D, one of the first 3D-LES of this flame type was presented by di Mare and Jones in 1999 [2] who applied simple steady flamelet model. Then a simplified Conditional Moment Closure (CMC) with the Conditional Source-term Estimation (CSE) proposed by Steiner and Bushe [3] was tested also on Sandia D. Very convincing results using unsteady-flamelet model were obtained by Pitsch and Steiner [4]. More recently the Conditional Moment Closure equations in the context of LES filtration were formulated by Navarro-Martinez et al. [5] and full CMC approach was validated using Sandia D flame. The LES-CMC approach was also applied by Garmory and Mastorakos [6] for Sandia D and F Flames. The results were very good for Sandia D Flame, however, application of the same settings to Sandia F Flame resulted in underprediction of the extent of local extinction. The LES with steady flamelet for Sandia D was also exploited by Kempf et al. [7] to study the structure of a diffusion flame in terms of length scales, scalar dissipation and flame orientation. A new premixed flamelet approach based on two additional equations for the mixture fraction and for the progress variable was proposed by Vreman et al. [8]. This in principle universal concept was validated on both premixed preheated Bunsen flame and non-premixed Sandia Flame D. The flamelet/progress variable model was also applied by Ihme and Pitsch [9,10] and used to predict extinction and reignition in Sandia Flames D and E. The concept of Steiner and Bushe [3] of the Conditional Source-term Estimation (CSE) was again applied by Ferraris and Wen [11] with some modifications reducing the number of flamelets and again validated on Sandia D. The models based on LES and transported PDF/FDF approach were also applied and validated using this flame. One of the first woks of this type was proposed by Sheikhi et. al. [12]. Bisetti and Chen [13] tested various mixing models using LES and Eulerian PDF method. Jones and Prasad [14] performed calculations for Sandia Flame D,E and F with LES and the Eulerian stochastic field method showing ability of the model to reproduce local extinction and reignition
Within the current Application Challenge attention is focused on the LES calculation only and neither RANS nor URANS predictions are analyzed.
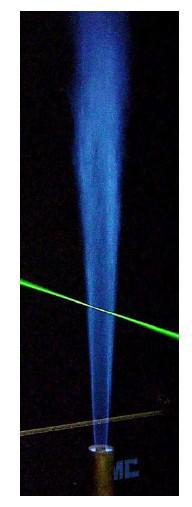

Fig.1. Sandia flame D - view of the flame (left); zoom of the vicinity of the nozzle (right)
Relevance to Industrial Sector
The Sandia D flame should be considered as general, very well documented non-premixed flame in the regime with little or no extinction. The CFD models the competency of which was judged with this AC can successfully be applied in industrial applications with similar Reynolds number in aeroengine combustion chambers or large scale furnaces in which due to safety reasons non-premixed flames are widely used. CFD models can be verified with the Sandia D flame in a comprehensive manner due to the availability of quantities carefully measured. The scalar measurements include: Raman/Rayleigh/LIF measurements of F, T, N2, O2, CH4, CO2, H2O, H2, CO, OH, and NO were obtained with a spatial resolution of 0.75 mm. Results include axial profiles in each flame (x/d = 5, 10, 15, ... , 80), radial profiles (x/d = 1, 2, 3, 7.5, 15, 30, 45, 60, 75). The measurements contain mean and fluctuating component scalar distributions. Moreover, measurements were performed for the velocity and temperature mean and fluctuating component fields. The measurements allow a verification of the turbulence model, the turbulence/combustion interaction model as well as the chemical kinetics relations applied.
Design or Assessment Parameters
An important parameter for CFD model validation of a non-premixed flame is the temperature profile along the jet flame axis. A characteristic feature of this profile is the maximum temperature i.e. its value and location.
The profiles of mean mixture fraction, mean mass fractions of methane and oxygen along the jet flame axis are characterized by a certain distance from the nozzle outlet over which the mass fraction of methane and oxygen remain constant showing the flame zone boundary. The same refers to water vapor and carbon dioxide. This distance can also be treated as DOAP.
The intermediate species taking part in the reaction steps such as hydrogen and carbon monoxide are characterized by the local maximum of the mean mass fraction profiles. The value of the maximum and its location is taken into account in CFD model validation.
Considering the fluctuating components of all parameters mentioned above, all are characterized by a local maximum so their value and location are also DOAPs.
For verification of the CFD results also the radial profiles at chosen cross sections should be used as DOAP. The mean axial velocity component and mixture fraction radial profiles have their maximum at the flow axis. As quantitative measure of the profile the half-radius can be taken. By contrast, the fluctuating components of the axial velocity component and mixture fraction have their maximum off the jet flame axis, and the value of the maximum and its location are taken as DOAP.
Flow Domain Geometry
Schematic view on the main and pilot burners located 15 cm above the vertical wind tunnel exit is shown in Fig.2. The flame is unconfined.
BURNER DIMENSIONS
| Main jet inner diameter, d | 7.2 mm |
| Pilot flame annulus inner diameter | 7.7 mm (wall thickness = 0.25 mm) |
| Pilot flame annulus outer diameter | 18.2 mm |
| Burner outer wall diameter | 18.9 mm (wall thickness = 0.35 mm) |
| Wind tunnel exit | 30x30 cm |

Flow Physics and Fluid Dynamics Data
Contributed by: Andrzej Boguslawski — Technical University of Częstochowa
© copyright ERCOFTAC 2024
