UFR 1-06 Description: Difference between revisions
m (Dave.Ellacott moved page SilverP:UFR 1-06 Description to UFR 1-06 Description) |
|||
| (250 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
}} | }} | ||
= Axisymmetric buoyant far-field plume | = Axisymmetric buoyant far-field plume = | ||
=== Underlying Flow Regime 1-06 === | |||
= Description = | = Description = | ||
| Line 18: | Line 15: | ||
This document focusses on the underlying flow of the fully-developed, steady, vertical, axisymmetric (round) plume flowing in a still and unstratified environment. This includes consideration of both rising, positively-buoyant plumes and falling, dense, negatively-buoyant plumes. Only turbulent plumes are considered as this covers nearly all relevant engineering and environmental applications. For a review of laminar plumes, see . | This document focusses on the underlying flow of the fully-developed, steady, vertical, axisymmetric (round) plume flowing in a still and unstratified environment. This includes consideration of both rising, positively-buoyant plumes and falling, dense, negatively-buoyant plumes. Only turbulent plumes are considered as this covers nearly all relevant engineering and environmental applications. For a review of laminar plumes, see . | ||
This UFR is relevant to the Application Challenges | This UFR is relevant to the Application Challenges AC4-03 on air flows in an open plan air-conditioned office, and AC4-04 on tunnel fires, and to UFR4-09 on confined buoyant plumes. | ||
== Overview of the UFR == | == Overview of the UFR == | ||
Free vertical buoyant plumes and free-jets are related phenomena, both having a core region of higher momentum flow surrounded by shear layers bounding regions of quiescent fluid. However, whereas for jets the driving force for the fluid motion is a pressure drop through an orifice, for plumes the driving force is buoyancy due to gradients in fluid density. Plumes can develop due to density gradients caused by temperature differences, for example in fires, or can be generated by fluids of different density mixing (e.g. hydrogen releases in air). There are many flows of both engineering and environmental importance that feature buoyant plumes, ranging from flows in cooling towers and heat exchangers to large geothermal events such as volcanic eruptions. For a good introduction to turbulent jets and plumes, see Chen & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[1]]] | Free vertical buoyant plumes and free-jets are related phenomena, both having a core region of higher momentum flow surrounded by shear layers bounding regions of quiescent fluid. However, whereas for jets the driving force for the fluid motion is a pressure drop through an orifice, for plumes the driving force is buoyancy due to gradients in fluid density. Plumes can develop due to density gradients caused by temperature differences, for example in fires, or can be generated by fluids of different density mixing (e.g. hydrogen releases in air). There are many flows of both engineering and environmental importance that feature buoyant plumes, ranging from flows in cooling towers and heat exchangers to large geothermal events such as volcanic eruptions. For a good introduction to turbulent jets and plumes, | ||
see Chen & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[1]]] | |||
or List [[UFR_1-06_References|[6]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[7]]]. | or List [[UFR_1-06_References|[6]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[7]]]. | ||
A more general discussion of buoyant flows is given in Gebhart ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[4]]]. | A more general discussion of buoyant flows is given in Gebhart ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[4]]]. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 39: | ||
{| | |||
}{\rho _{\infty }}\right)\right]}}</math></ | |- | ||
|width="750" align="center"|<math>{Fr}=\frac{U}{\sqrt{\left[gD\left(\frac{\rho _{\infty }-\rho | |||
}{\rho _{\infty }}\right)\right]}}</math> | |||
|width="40" align="right"|<math>\left(1\right)</math> | |||
|} | |||
where ''U'' is the mean velocity, ''g'' gravity, ''D'' a characteristic length-scale, and ''ρ'' density. Subscript ∞ refers to the far-field value | |||
<ref name="ftn1">In some cases, the densimetric Froude number is defined with the density difference | |||
made dimensionless using the plume source density, ''ρ, ''instead of the ambient density | |||
''ρ<sub>∞</sub>, ''e.g. | |||
Chen & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[1]]] | |||
and Hossain & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[8]]].</ref> | |||
The Froude number represents the ratio of inertial forces to buoyancy forces. It ranges in value from near zero for pure plumes, towards infinity for jets with negligible buoyancy. Chen & Rodi analysed a number of jet and plume experiments and, using dimensional analysis, produced the graph reproduced in Figure 2, which shows the transition from jet- to plume-like behaviour with increasing ''Fr''. | |||
<ref name="ftn2">The local Froude number in this case is evaluated on the plume centreline. | |||
Note, the ''Fr'' defined by Chen & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[1]]] | |||
is the square of the definition of ''Fr'' given above.</ref> | |||
Figure 2 shows how the difference in mean density between the axis of the plume and the far field value decays with distance from the inlet. In the jet-like region near the source, the density difference decays at a rate (''x'' – ''x''<sub>0</sub>)<sup>-1 </sup>whereas in the fully-developed plume region it decays faster at (''x'' – ''x''<sub>0</sub>)<sup>-5/3</sup>. Here, ''x'' is the axial coordinate and ''x''<sub>0</sub> is the “virtual” source location, see Figure 1. Empirical correlations for the decay rate of mean velocity and scalars in buoyant jets are given in Gebhart ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[4]]]. Both jets and plumes spread linearly in a uniform environment, although at different rates. Empirical correlations for the spreading rate in plumes are given later. | |||
Another common measure used to assess when buoyant jets reach a fully-developed state is the Morton length scale, <math>l_M</math>: | |||
< | {| | ||
|- | |||
|width="750" align="center"|<math>l_M=\frac{M_0^{3/4}}{F_0^{1/2}}</math> | |||
|width="40" align="right"|<math>\left(2\right)</math> | |||
|} | |||
| Line 60: | Line 75: | ||
< | {| | ||
|- | |||
|width="750" align="center"|<math>M_0=2\pi\int_0^{r_0}U^2 r\ dr\qquad\qquad | |||
F_0=2\pi\int_0^{r_0}Ug\frac{\Delta\rho}{\rho_\infty}r\ dr</math> | |||
|width="40"" align="right"|<math>\left(3\right)</math> | |||
|} | |||
| Line 66: | Line 86: | ||
< | {| | ||
|- | |||
|width="750" align="center"|<math>l_m=\frac{F r_0 D}{(\pi/4)^{1/4}}</math> | |||
|width="40" align="right"|<math>\left(4\right)</math> | |||
|} | |||
where ''Fr''<sub>0</sub> is the the source densimetric Froude number at the source and ''D'' the inlet source diameter. | where ''Fr''<sub>0</sub> is the the source densimetric Froude number at the source and ''D'' the inlet source diameter. | ||
[[Image:]] | [[Image:UFR1-06_figure2.png|center|400px]] | ||
<center>'''Figure 2 '''Decay of centreline density in round plumes from Chen & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[1]]]</center> | |||
< | Papanicolau & List [[UFR_1-06_References|[9]]] suggest that jet-like conditions occur in turbulent buoyant jets for <math>(x-x_0)/l_m<1</math>and fully-developed plume-like conditions for <math>(x-x_0)/l_m>5</math>. However, there is some debate in the literature over the distance required to reach fully-developed plume conditions, see for example Dai ''et al'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]] and Shabbir & George [[UFR_1-06_References|[11]]]. Mean parameters (velocity, temperature etc.) require a shorter distance to reach a fully-developed state than statistical quantities such as Reynolds stresses. | ||
An important feature of the mean flow in the fully-developed region of turbulent buoyant plumes is “self-similarity” or “self-preserving” behaviour. In positively-buoyant plumes, as the less dense fluid rises and spreads, the mean velocity peak on the plume centreline decays and the plume becomes wider. However, the shape of the mean velocity profile remains the same. If the dimensionless radial profiles of the mean velocity are plotted at different vertical positions in the plume on the same graph axes, the curves all fall on top of one another. Self-similarity is also exhibited in the dimensionless temperature and species concentration profiles and in the dimensionless RMS turbulent fluctuations of velocity, temperature and concentration | |||
<math>\left(\sqrt{u^2}/U_0\right.</math>, <math>\sqrt{\nu^2}/U_0</math>, <math>\sqrt{\theta^2}/\Theta_0</math> or <math>\left.\sqrt{c^2}/C_0\right)</math>. | |||
Sample data from the experiments of Papanicolaou & List [[UFR_1-06_References|[9]]] and Dai ''et al'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]] shown in Figures 3 and 4 demonstrate this behaviour. | |||
[[Image:UFR1-06_figure3.gif|center|700px]] | |||
<center>'''Figure 3 '''Dimensionless mean velocity and mean concentrations profiles in a turbulent axisymmetric plume, from Papanicolaou & List [[UFR_1-06_References|[9]]]</center> | |||
[[Image:UFR1-06_figure4.gif|center|400px]] | |||
[[ | <center>'''Figure 4 '''Dimensionless mixture fraction fluctuation profiles in a turbulent axisymmetric plume, from Dai ''et al'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]]</center> | ||
<center>''' | |||
=== Plume Analysis Based on Integral Equations === | |||
One means of analysing the flow behaviour of self-similar buoyant plumes is to use integral methods. This involves assuming profiles for the velocity, temperature and concentration based on experimental observations. The mean flow equations are then integrated over the whole plume cross-section to produce ordinary differential equations. The entrainment rate is also assumed, usually as a function of the local centreline velocity. | |||
Theoretical analysis of self-similar plumes using integral methods began more than 50 years ago with the | |||
works of Yih [[UFR_1-06_References|[12]]], Rouse ''et al'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[13]]], | |||
Batchelor [[UFR_1-06_References|[14]]] and Morton ''et al'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[15]]] | |||
for plumes with small density differences in unstratified and stratified environments. More recently, these theories have been extended to consider plumes with significant density | |||
differences [[UFR_1-06_References|[16]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[17]]], | |||
with unsteady source strengths | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[18]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[19]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[20]]] | |||
and fire plumes [[UFR_1-06_References|[21]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[22]]] | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[23]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[24]]]. | |||
The simplest analysis proceeds by assuming that the velocity and buoyancy force are constant across the plume and zero outside it (i.e. a 'top hat' profile). Transport equations for the conservation of volume, momentum and density deficit are integrated analytically with respect to the vertical distance, ''x'', to arrive at expressions for the plume radius, ''b'', the vertical velocity, ''U''<span style="font-style: normal">, and the density, ''ρ'', inside the plume | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
|width="750" align="center"|<math>b=\frac{6}{5}\alpha x\qquad U=\frac{5}{6\alpha} | |||
\left(\frac{9}{10}\alpha Q\right)^{1/3}x^{-{1/3}}\qquad | |||
g\frac{(\rho_1-\rho)}{\rho_1}=\frac{5Q}{6\alpha}\left(\frac{9}{10}\alpha Q\right)^{-{1/3}}x^{-{5/3}} | |||
</math> | |||
|width="40" align="right"|<math>\left(5\right)</math> | |||
|} | |||
where ''ρ''<sub>1</sub> is a reference density, ''α'' is an empirical entrainment coefficient and ''Q'' is the buoyancy flux, given by: | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
|width="750" align="center"|<math>Q=b^2Ug\left(\frac{\rho_1-\rho}{\rho_1}\right)</math> | |||
|width="40" align="right"|<math>\left(6\right)</math> | |||
|} | |||
The empirical entrainment coefficient, ''α'', relates the entrainment velocity, ''U''<sub>''e''</sub>, to the plume velocity (''U''<sub>''e''</sub> = ''αU''). This analysis was first published by Schmidt | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[25]]] and is described in Morton ''et al'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[15]]]. | |||
Morton ''et al'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[15]]] extended the above approach, assuming Gaussian radial profiles for the velocity and buoyancy force instead of top-hat profiles. They found that the spreading rate of the plume (d''b''/d''x'') was equal to 6''α''/5 and was independent of the strength of the buoyancy source. In their analysis they defined the plume radius, ''b'', as the point where the velocity fell to e<sup>-1</sup> | |||
of its centreline value (0.37''U''<sub>''c''</sub>). | |||
Experiments undertaken by Morton ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[15]]] of positively buoyant plumes in stratified saline solutions found the entrainment coefficient to be around ''α'' = 0.093. More recent studies have suggested a value of ''α'' ≈ 0.082 for plumes in unstratified environments (for comparison, the entrainment constant for pure jets | |||
is ''α'' ≈ 0.057) [[UFR_1-06_References|[4]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[26]]]. | |||
Recently, Diez & Dahm [[UFR_1-06_References|[27]]] developed an alternative integral approach that does not rely upon the entrainment coefficient, ''α''. Instead, it uses the integral equation for the momentum flux to develop an equation for the local centreline velocity. Diez & Dahm's model relies upon a parameter, ''c''<sub>''δ''</sub>, which experiments show to be constant in the far-field of both jets and plumes. | |||
Further details of integral methods applied to plumes and jets, including discussion of empirical models for ''α '' as a function of the Froude number, can be found in Chen & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[1]]] and Gebhart ''et al'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[4]]]. | |||
Whilst integral methods can provide accurate results for relatively simple plumes it is difficult to extend the approach to model more complex turbulent flows, where for example the plume may hit a wall or encounter regions of flow recirculation. To study these more complex flows, a more general-purpose CFD approach must be used. | |||
== Review of UFR studies and choice of test case == | == Review of UFR studies and choice of test case == | ||
CFD simulations of fully-developed, self-similar turbulent buoyant plumes | |||
have, to date, mainly solved the Reynolds-Averaged Navier Stokes | |||
(RANS) equations. Whilst Large Eddy Simulation (LES) can in theory be | |||
used to study such flows, it involves significantly greater computing | |||
resources. To the author's knowledge, the only study of the far-field, | |||
self-similar behaviour of plumes using LES is that undertaken by | |||
Zhou ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[28]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[29]]]. | |||
They simulated the thermal plumes of George ''et al.'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] and | |||
Shabbir & George [[UFR_1-06_References|[11]]] | |||
in [[UFR_1-06_References|[28]]] and those of Cetegen [[UFR_1-06_References|[30]]] | |||
in [[UFR_1-06_References|[29]]]. Whilst axisymmetric RANS simulations of these flows | |||
would involve meshes with around 4,000 cells, the large-eddy | |||
simulations of Zhou ''et al.'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[28]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[29]]] | |||
used more than 4 million cells. | |||
Before describing the experimental and CFD studies on which this UFR | |||
documentation will be based, a brief review is provided below of | |||
other studies of the axisymmetric buoyant plume which, for various | |||
reasons, have not been adopted here. | |||
=== Review of the nearly-relevant work === | |||
==== Experiments ==== | |||
There have been numerous experimental studies of the turbulent buoyant plume. A major review was undertaken by Chen & Rodi in 1980 [[UFR_1-06_References|[1]]]. | |||
They provided recommended values for the spreading rates of the plume based on the momentum and temperature or concentration of <math>dr_{U_{1/2}}/dx=0.112</math> and | |||
<math>dr_{f_{1/2}}/dx=0.104</math>. The momentum value <math>\left(dr_{U_{1/2}}/dx\right)</math> | |||
was based on the experiments of | |||
George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] | |||
which were considered to be the most consistent of the reviewed data. | |||
Following Chen & Rodi's review, in the late 1980's and early 90's, Shabbir, George and Taulbee at the University of Buffalo published a number of papers on buoyant plume experiments | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[31]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[32]]] | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[33]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[34]]]. | |||
In [[UFR_1-06_References|[33]]] they compared the magnitude of various terms in the ''k'' – ''ε'' model equations to values obtained directly from experiments. A particularly significant finding was that the streamwise heat flux, <math>\overline{uT}</math>, was underpredicted by a factor of four using the standard ''k'' – ''ε'' model with the Simple Gradient Diffusion Hypothesis (SGDH) (described later). Apart from this shortcoming, however, the ''k'' – ''ε'' model was found to perform reasonably well. | |||
More recently, Dai ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]] performed experiments using negatively-buoyant plumes of CO<sub>2</sub> and SF<sub>6</sub> in air. A summary table, comparing their results for the axisymmetric buoyant plume against those of Papantoniou & List [[UFR_1-06_References|[35]]], | |||
Papanicolaou & List [[UFR_1-06_References|[9]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[36]]], | |||
Shabbir & George [[UFR_1-06_References|[34]]] | |||
and George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] is reproduced in Table 1a. | |||
<center>'''Table 1a''' Summary of self-preserving buoyant plume properties, from Dai ''et al.'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]]</center> | |||
[[Image:UFR1-06_table1a.gif|center|650px]] | |||
<center>'''Table 1b''' Densimetric Froude numbers for the experiments given in Table 1a, calculated using Equation (1).</center> | |||
{|align="center" | |||
|- | |||
|'''''Source'''''||width="30"| ||align="center"|'''''Fr<sub>0</sub>''''' | |||
|- | |||
|colspan="3" height="5px" style="border-top:2px solid black;"| | |||
|- | |||
|Dai ''et al.'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]]||width="30"| ||align="center"|3.75, 7.80 | |||
|- | |||
|Papantoniou and List (1989)||width="30"| ||align="center"|1.89, 2.24 | |||
|- | |||
|Papanicolaou and List (1988)||width="30"| ||align="center"|0.87 to 3.88 | |||
|- | |||
|Papanicolaou and List (1987)||width="30"| ||align="center"|0.41 to 7.79 | |||
|- | |||
|Shabbir and George (1992)||width="30"| ||align="center"|1.60, 1.80 | |||
|- | |||
|George ''et al.'' (1977)||width="30"| ||align="center"|1.23 | |||
|} | |||
The third and fourth columns of Table 1a define the extent of the fully-developed flow regions in the axial | |||
direction made dimensionless using the source diameter, ''d'', and the Morton length scale, ''l''<sub>M.</sub>. | |||
Dai ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[37]]] | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[38]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[39]]], | |||
suggested that the large range in values of (''x ''- ''x''<sub>0</sub>)/''l''<sub>M</sub> | |||
shown in Table 1a is due to the fact that many researchers had incorrectly made measurements of transitional | |||
plumes exhibiting quasi-jet-like behaviour, rather than fully-developed, self-similar plumes. They attributed | |||
this partly to the difficulty in measuring concentrations accurately at significant distances from the source | |||
due to the relatively fast (''x'' – ''x''<sub>0</sub>)<sup>-5/3 </sup>decay rate of scalars in plumes. They | |||
also noted that flow velocities in plumes are relatively low compared to jets, and so greater care had to be | |||
taken in the far field to prevent small external disturbances affecting measurements. | |||
This matter was disputed by Shabbir & George [[UFR_1-06_References|[11]]] | |||
and George [[UFR_1-06_References|[40]]] | |||
who noted that plume measurements | |||
are strongly influenced by ambient thermal stratification. Since stratification is more difficult to control | |||
the further ones goes from the source, this could potentially affect measurements taken at larger axial | |||
distances, such as those taken by | |||
Dai ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[37]]] | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[38]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[39]]] | |||
at distances of ''z''/''D'' up to 151. In a neutral environment, | |||
conservation of energy implies conservation of buoyancy [[UFR_1-06_References|[1]]]. | |||
One means to check whether ambient thermal | |||
stratification has adversely affected measurements is therefore to ensure that buoyancy is conserved. | |||
Shabbir & George [[UFR_1-06_References|[11]]] | |||
carefully determined the rate of buoyancy added at the source and found that in their | |||
measurements, buoyancy was conserved to within 10%. | |||
The other columns in Table 1a provide details of the shape of the self-similar profiles of the scalar | |||
within the fully-developed region. | |||
The radial mean scalar profiles were approximated using a Gaussian profile: | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
|width="750" align="center"|<math> | |||
F\left(\frac{r}{x-x_0}\right)=F(0)\exp\left[-k_f^2\left(\frac{r}{x-x_0}\right)^2\right] | |||
</math> | |||
|width="40" align="right"|<math>\left(7\right)</math> | |||
|} | |||
To obtain self-similar profiles, the mean properties were then scaled using the following formula, | |||
from List [[UFR_1-06_References|[6]]]: | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
|width="750" align="center"|<math> | |||
\overline{f}=\left(\frac{\pi Fr_0}{4}\right)^{2/3}\left(\frac{\rho}{\rho_0}\right) | |||
\left(\frac{x-x_0}{D}\right)^{-{5/3}}F\left(\frac{r}{x-x_0}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
|width="40" align="right"|<math>\left(8\right)</math> | |||
|} | |||
The final two columns in Table 1a provide centreline values of the dimensionless | |||
mean scalar, ''F''(0), and RMS scalar fluctuations, | |||
<math>\left(\overline{f^\prime}/\overline{f}\right)_c</math>, | |||
for the various | |||
experiments. The sixth column provides details of the spreading rate of the plume, denoted | |||
<math>l_f/{(x-x_0)}</math>, where <math>l_f</math> is the plume radius as defined by the point | |||
where <math>\overline{f}</math> falls to e<sup>-1</sup> of its centreline value. | |||
The experiments undertaken by | |||
Dai ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[37]]] | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[38]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[39]]] | |||
indicated that self-similar round turbulent plumes were up to 40% narrower and had mean | |||
centreline scalar values and streamwise velocities that were up to 30% larger than were previously thought. | |||
This finding was confirmed by a later study by the same group using the same | |||
experimental arrangements [[UFR_1-06_References|[41]]]. | |||
The paper by Brescianini & Delichatsios [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]] provides cross-plots of both Dai ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]] and | |||
George ''et al'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] velocity profiles. | |||
These show that on a graph of velocity, ''U'', versus radial location | |||
''r''/(''x'' – ''x''<sub>0</sub>), the experimental profile from | |||
George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]] is significantly | |||
flatter and wider than the more recent data of | |||
Dai ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]]. However, when plotted in dimensionless | |||
form (''U''/''U''<sub>c</sub> versus ''r''/''r''<sub>1/2</sub>) the data are remarkably similar. | |||
In 1994, Shabbir & George [[UFR_1-06_References|[11]]] | |||
repeated the earlier experiments of | |||
George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] with the joint | |||
aim of reproducing the earlier experiments under stricter laboratory conditions and investigating the budgets | |||
of the mean energy and momentum equations. The peak mean values and plume half-widths were found to be in good | |||
agreement with their earlier work | |||
(see also Heskestad [[UFR_1-06_References|[43]]] for comparisons). | |||
Shabbir & Taulbee [[UFR_1-06_References|[44]]] recently provided further analysis | |||
of the budgets for the turbulent heat flux and Reynolds stress | |||
transport equations to help with the development | |||
of new second-moment closure models. They found that the “local equilibrium assumption” | |||
(where production and dissipation are in balance) provided a reasonable approximation for the turbulent heat flux transport equation | |||
but that convection and diffusion terms were significant in the Reynolds stress budgets. This finding has | |||
implications for the development of algebraic stress models (see later). ''A priori'' assessment of simple | |||
pressure-correlation models for the turbulent heat flux and Reynolds stress equations were also presented in | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[44]]]. | |||
They found that the measured axial heat flux, | |||
<math>\overline{uT}</math>, | |||
was generally | |||
several times larger than that modelled by a simple Boussinesq gradient diffusion form and proposed an | |||
algebraic stress model to improve its prediction. | |||
A recent experimental study by Yao & Marshall [[UFR_1-06_References|[45]]] | |||
used Planar Laser Induced Fluorescence (PLIF) to investigate turbulent buoyant salt-water plumes. | |||
Results were given for the fully-developed region extending approximately from 6 < (''x''-''x''<sub>0</sub>)/''D'' < 30, | |||
where the mean plume radius was found to increase linearly and the dimensionless | |||
density difference decay according to the -5/3 law. Velocity measurements were not made. Dimensionless RMS | |||
concentration fluctuations varied between 0.35 and 0.45, in fair agreement with the earlier experiments | |||
reported in Table 1a. The purpose of Yao & Marshall's measurements was to simulate fire plumes. However, as | |||
they noted, care should be taken in interpreting data from salt-water experiments since the Schmidt number in | |||
liquid plumes is nearly three orders of magnitude larger than the corresponding value in gaseous plumes. The | |||
effect of this higher Schmidt number is to inhibit scalar mixing at small scales and near walls, where | |||
molecular diffusion is significant. | |||
The review paper by Heskestad [[UFR_1-06_References|[43]]], | |||
discussed briefly the variability in reported measured peak values and | |||
spreading rates in axisymmetric plume experiments, shown in Table 2. Heskestad's earlier | |||
fire plume measurements [[UFR_1-06_References|[22]]], | |||
were in reasonably good agreement with the measurements of | |||
George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]]. | |||
For the spreading rate of the plume, Heskestad [heske98] commented | |||
that the | |||
George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] | |||
and Shabbir & George [[UFR_1-06_References|[11]]] | |||
experiments were considered the most reliable. | |||
Chen & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[1]]] | |||
also considered the work of | |||
George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] | |||
to be the most consistent of their reviewed data. | |||
<center>'''Table 2''' Summary of experimental plume characteristics from Heskestad [[UFR_1-06_References|[43]]]</center> | |||
{|align="center" | |||
|- | |||
|width="200"|'''''Study''''' | |||
|align="center"|'''''Centreline velocity, U<sub>0</sub>''''' | |||
|align="center"|'''''Half-width based on velocity, b<sub>U</sub>''''' | |||
|align="center"|'''''Centreline temperature difference, ΔT<sub>0</sub>''''' | |||
|align="center"|'''''Half-width based on temperature, b<sub>ΔT</sub>''''' | |||
|- | |||
|colspan="5" height="5px" style="border-top:2px solid black;"| | |||
|- | |||
|Hesketad [[UFR_1-06_References|[22]]] | |||
|align="center"|3.4||align="center"|—||align="center"|9.1||align="center"|0.12 | |||
|- | |||
|George ''et al.'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] | |||
|align="center"|3.4||align="center"|1.08||align="center"|9.1||align="center"|0.104 | |||
|- | |||
|Shabbir & George [[UFR_1-06_References|[11]]] | |||
|align="center"|3.4||align="center"|1.07||align="center"|9.4||align="center"|0.10 | |||
|- | |||
|Papanicolaou & List [[UFR_1-06_References|[9]]] | |||
|align="center"|3.9||align="center"|—||align="center"|14.3||align="center"|0.09 | |||
|- | |||
|Dai ''et al.'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[10]]] | |||
|align="center"|—||align="center"|—||align="center"|12.6||align="center"|0.08 | |||
|} | |||
==== CFD Studies ==== | |||
One of the most comprehensive early CFD studies of buoyant plumes was undertaken by | |||
Hossain & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[8]]]. | |||
They examined the performance of an algebraic stress and heat flux model in axisymmetric and plane plumes, | |||
buoyant jets and pure jets. Their model was based on the differential stress model of | |||
Gibson & Launder [[UFR_1-06_References|[46]]] | |||
which is described in some detail in their paper. They showed how the differential model was simplified to | |||
algebraic expressions by neglecting the convective and diffusive fluxes, effectively assuming that the flow | |||
only evolves slowly (i.e. local equilibrium). The validity of this assumption in buoyant plumes was examined | |||
subsequently by | |||
Shabbir & Taulbee [[UFR_1-06_References|[33]]]. | |||
The proposed algebraic model shared some features with the standard | |||
''k'' – ''ε'' model but used modified expressions for the stresses and heat fluxes and a more sophisticated | |||
diffusion term. An important feature of the model was that the coefficients appearing in the eddy viscosity and | |||
diffusivity were functions of buoyancy parameters (not the case with the standard ''k'' – ''ε'' model). The | |||
model also incorporated an empirical correction for the round-jet/plane-jet anomaly first proposed by | |||
Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[47]]]. | |||
The buoyancy term in the modelled ''ε-''equation was empirical in nature and | |||
Hossain & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[8]]] | |||
acknowledged that it would not be well suited to more general flow situations. To simulate the axisymmetric | |||
plume, they used a parabolic method where the numerical grid adjusted itself to the increase in plume width | |||
using a dimensionless stream function as a lateral coordinate. Both the limiting cases of pure jets and pure | |||
plumes were well predicted by the algebraic model as was the transition between jet and plume-behaviour in | |||
buoyant jets. | |||
A number of more recent CFD simulations of axisymmetric buoyant plumes have also used variants of the | |||
standard ''k – ε'' turbulence model. | |||
Nam & Bill [[UFR_1-06_References|[48]]] | |||
performed simulations of pool fires using the commercial | |||
code PHOENICS and modified the standard | |||
Launder & Spalding [[UFR_1-06_References|[49]]] | |||
model by changing, arbitrarily, the values of | |||
the effective Prandtl number, ''σ''<sub>''eff''</sub>, and the model constant, ''c''<sub>''μ''</sub>, from 1.0 | |||
and 0.09 to 0.614 and 0.109, respectively, to obtain improved results in buoyant plumes. They then used their | |||
modified model to simulate buoyant ceiling jets and found results to be slightly better than with the standard | |||
model. The consequences of changing these constants on the model's performance in other flows was not explored. | |||
Hara & Kato [[UFR_1-06_References|[50]]] | |||
used a standard ''k – ε'' model and presented results using different meshes with | |||
various modifications to the ''c''<sub>''ε3''</sub> constant in the buoyancy production term of the | |||
''ε-''equation. They compared results to the experiments of | |||
Yokoi [[UFR_1-06_References|[51]]], | |||
which involved releases of buoyant | |||
fluid through a circular orifice, but modelled this as a square orifice to enable the use of hexahedral | |||
Cartesian grids. Results were found to be grid-sensitive and recommendations regarding resolution were | |||
provided. Differences in the ''c''<sub>''ε3''</sub> constant were found to have no effect on results. | |||
The study by Brescianini & Delichatsios [[UFR_1-06_References|[42]]] | |||
also examined the ''k – ε'' model in combination with different | |||
sub-models for the turbulence production due to buoyancy, including the Boussinesq Simple Gradient Diffusion | |||
Hypothesis (SGDH), the Generalized Gradient Diffusion Hypothesis (GGDH) of | |||
Daly & Harlow [[UFR_1-06_References|[52]]] and the | |||
algebraic model of Hossain & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[8]]]. | |||
The SGDH and GGDH models are described in detail later in this | |||
UFR. They compared CFD predictions mainly to the experimental measurements of | |||
Dai ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[41]]] and | |||
examined both axisymmetric and plane plumes. None of the model variants were found to capture all the flow | |||
details of both axisymmetric and plane plumes and no firm conclusions were drawn regarding the best turbulence | |||
buoyancy production model. The GGDH model was found to give improved predictions of the streamwise mass flux | |||
compared to SGDH. | |||
The Hossain & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[8]]] | |||
model was also found sometimes to produce better results than | |||
GGDH. However, Brescianini & Delichatsios [[UFR_1-06_References|[42]]] | |||
noted that the Hossain & Rodi [[UFR_1-06_References|[8]]] | |||
model was sensitive | |||
to the model constants and was more complex to implement. They concluded that given the overall satisfactory | |||
performance of the ''k – ε'' model in predicting the mean-flow quantities, there was no real advantage to be | |||
gained in using a higher-order closure model to study buoyant plumes. | |||
Yan & Holmstedt [[UFR_1-06_References|[53]]] | |||
compared two ''k – ε'' model variants against the | |||
George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] | |||
experiments for the axisymmetric plume. The first variant was a standard ''k – ε'' model with SGDH and the | |||
second involved an additional algebraic stress model for the production term in the ''k''-equation combined | |||
with GGDH for the production due to buoyancy. The additional algebraic stress model was based on a | |||
second-moment-closure correction devised by | |||
Davidson [[UFR_1-06_References|[54]]] | |||
The ''k – ε'' model with SGDH was found to underpredict the spreading rate of the plume, producing overly-high | |||
temperatures and velocities in the core. Their modified model produced better results for the axisymmetric | |||
plume. They went on to examine buoyant diffusion flames using their new approach. | |||
Malin & Younis [[UFR_1-06_References|[55]]] | |||
also compared CFD predictions to the George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]] | |||
data but used second-moment-closure models and the parabolic PHOENICS solver. The objective of Malin & Younis's | |||
study was to extend the second-moment closure model of | |||
Gibson & Younis | |||
[[UFR_1-06_References|[56]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[57]]][[UFR_1-06_References|[58]]] to buoyant flows | |||
and examine its performance in free turbulent jets and plumes. The model produced good predictions of the mean | |||
axial velocity and temperature profiles and was able to capture, at least qualitatively, the anisotropy in the | |||
Reynolds stresses. | |||
Van Maele & Merci [[UFR_1-06_References|[2]]] | |||
recently examined both an axisymmetric and a plane buoyant wall plume using SGDH and GGDH variants of the | |||
standard ''k – ε '' model and a realizable ''k – ε '' model with the commercial code, Fluent. The SGDH source | |||
term was shown to have little effect in the axisymmetric plume case, and consequently the turbulent kinetic | |||
energy was underpredicted and the centreline velocity and temperature were overpredicted. The GGDH model was | |||
found to perform well with either of the two ''k – ε '' model variants. For the axisymmetric plume case, | |||
results were compared to the experimental data of | |||
George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]]. | |||
Finally, Craft ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[59]]] | |||
mentioned briefly the results for the buoyant plume in discussing developments of their Two-Component Limit | |||
(TCL) second-moment-closure model. Predictions using the TCL model were compared to the experiments of | |||
Cresswell ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[60]]] | |||
and results from a “basic” second-moment-closure model. The spreading rate of the self-similar buoyant plume | |||
was found to be better predicted using the more sophisticated TCL model. | |||
==== Parabolic Solvers ==== | |||
A number of the early CFD studies discussed above used a parabolic or space-marching solution method. This involves the solution of simplified boundary-layer-type transport equations. Comparisons of model predictions using parabolic and elliptic codes for jets and plumes are given | |||
by El Baz ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[61]]], | |||
Magi ''et al.'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[62]]] | |||
and Haroutunian & Launder [[UFR_1-06_References|[63]]]. | |||
In axisymmetric free-jets, El Baz ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[61]]] | |||
and Magi ''et al.'' [[UFR_1-06_References|[62]]] | |||
found that the use of an elliptic instead of a parabolic approach resulted in differences in the predicted spreading rates of 10% or more. In axisymmetric buoyant plumes, | |||
Haroutunian & Launder [[UFR_1-06_References|[63]]] | |||
found that spreading rates differed by only a few percent, but second moments differed by more than 30% in some cases. Given the capabilities of current desktop computers, there is no longer a need on the grounds of grid-resolution and computing time to use a parabolic solver in far-field plume simulations. However, care must be taken when using elliptic codes to ensure that the solution is not restricted or influenced by the side entrainment boundaries. | |||
=== Studies on which this UFR review will be based === | |||
The work of Van Maele & Merci [[UFR_1-06_References|[2]]] | |||
has been chosen as providing the most appropriate currently available information on which comparisons have been made between CFD and experiment. Their study represents a good match for what is required for this UFR. They examined SGDH and GGDH variants of the both the standard ''k – ε '' model and a realizable ''k – ε '' model using the commercial CFD software, Fluent. The paper provides a thorough description of methodology used, including description of the numerical methods and a grid-dependence study. Both axisymmetric and plane wall plumes were examined, the former using the | |||
experimental data of George ''et al''. [[UFR_1-06_References|[3]]]. | |||
The methodology used in their studies is described below. | |||
== Footnotes == | |||
<references/> | |||
{{UFRHeader | {{UFRHeader | ||
| Line 99: | Line 553: | ||
{{ACContribs | {{ACContribs | ||
| authors=Simon Gant | | authors=Simon Gant | ||
| organisation= | | organisation=UK Health & Safety Laboratory | ||
}} | }} | ||
© copyright ERCOFTAC | © copyright ERCOFTAC 2010 | ||
Latest revision as of 19:11, 11 February 2017
Axisymmetric buoyant far-field plume
Underlying Flow Regime 1-06
Description
Preface
This document focusses on the underlying flow of the fully-developed, steady, vertical, axisymmetric (round) plume flowing in a still and unstratified environment. This includes consideration of both rising, positively-buoyant plumes and falling, dense, negatively-buoyant plumes. Only turbulent plumes are considered as this covers nearly all relevant engineering and environmental applications. For a review of laminar plumes, see .
This UFR is relevant to the Application Challenges AC4-03 on air flows in an open plan air-conditioned office, and AC4-04 on tunnel fires, and to UFR4-09 on confined buoyant plumes.
Overview of the UFR
Free vertical buoyant plumes and free-jets are related phenomena, both having a core region of higher momentum flow surrounded by shear layers bounding regions of quiescent fluid. However, whereas for jets the driving force for the fluid motion is a pressure drop through an orifice, for plumes the driving force is buoyancy due to gradients in fluid density. Plumes can develop due to density gradients caused by temperature differences, for example in fires, or can be generated by fluids of different density mixing (e.g. hydrogen releases in air). There are many flows of both engineering and environmental importance that feature buoyant plumes, ranging from flows in cooling towers and heat exchangers to large geothermal events such as volcanic eruptions. For a good introduction to turbulent jets and plumes, see Chen & Rodi [1] or List [6][7]. A more general discussion of buoyant flows is given in Gebhart et al. [4].
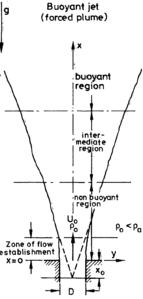
A free vertical buoyant plume can be split into a number of regions, see Figure 1. Close to the source, the flow is affected by details of the particular release conditions. This could include inertial effects if, for example, the flow involves a release of buoyant fluid through a nozzle under pressure, or, perhaps, other complexities associated with combustion in fire plumes. At a sufficient distance further downstream, the effects of the source conditions are lost, buoyancy forces dominate the flow and it exhibits plume behaviour. Between the near-source and far-field regions, there is a transitional region.
Plumes arising from continuous releases of buoyant fluid with significant initial momentum are classified as forced plumes or buoyant jets. Those involving a discrete release of buoyant fluid are termed thermals or puffs (e.g. as caused by an explosion), and starting plumes refer to the advancing front from a continuous buoyancy source in the initial phase of the release before a steady plume becomes established.
Buoyant jets (i.e. plumes with significant initial momentum) occur in a number of important practical applications such as the flow from smokestacks and cooling-water discharges into reservoirs. It is important in these cases to be able to identify when the transition occurs from jet-like behaviour near the source to plume-like behaviour in the far field. A common dimensionless parameter used to distinguish these two flow regions is the densimetric Froude number, Fr, given by:
where U is the mean velocity, g gravity, D a characteristic length-scale, and ρ density. Subscript ∞ refers to the far-field value
[1]
The Froude number represents the ratio of inertial forces to buoyancy forces. It ranges in value from near zero for pure plumes, towards infinity for jets with negligible buoyancy. Chen & Rodi analysed a number of jet and plume experiments and, using dimensional analysis, produced the graph reproduced in Figure 2, which shows the transition from jet- to plume-like behaviour with increasing Fr.
[2]
Figure 2 shows how the difference in mean density between the axis of the plume and the far field value decays with distance from the inlet. In the jet-like region near the source, the density difference decays at a rate (x – x0)-1 whereas in the fully-developed plume region it decays faster at (x – x0)-5/3. Here, x is the axial coordinate and x0 is the “virtual” source location, see Figure 1. Empirical correlations for the decay rate of mean velocity and scalars in buoyant jets are given in Gebhart et al. [4]. Both jets and plumes spread linearly in a uniform environment, although at different rates. Empirical correlations for the spreading rate in plumes are given later.
Another common measure used to assess when buoyant jets reach a fully-developed state is the Morton length scale, :
where M0 and F0 are the specific momentum and buoyancy added at the source of the plume:
For plumes with uniform properties at the source, this is equivalent to:
where Fr0 is the the source densimetric Froude number at the source and D the inlet source diameter.
Papanicolau & List [9] suggest that jet-like conditions occur in turbulent buoyant jets for and fully-developed plume-like conditions for . However, there is some debate in the literature over the distance required to reach fully-developed plume conditions, see for example Dai et al [10] and Shabbir & George [11]. Mean parameters (velocity, temperature etc.) require a shorter distance to reach a fully-developed state than statistical quantities such as Reynolds stresses.
An important feature of the mean flow in the fully-developed region of turbulent buoyant plumes is “self-similarity” or “self-preserving” behaviour. In positively-buoyant plumes, as the less dense fluid rises and spreads, the mean velocity peak on the plume centreline decays and the plume becomes wider. However, the shape of the mean velocity profile remains the same. If the dimensionless radial profiles of the mean velocity are plotted at different vertical positions in the plume on the same graph axes, the curves all fall on top of one another. Self-similarity is also exhibited in the dimensionless temperature and species concentration profiles and in the dimensionless RMS turbulent fluctuations of velocity, temperature and concentration
, , or .
Sample data from the experiments of Papanicolaou & List [9] and Dai et al [10] shown in Figures 3 and 4 demonstrate this behaviour.
Plume Analysis Based on Integral Equations
One means of analysing the flow behaviour of self-similar buoyant plumes is to use integral methods. This involves assuming profiles for the velocity, temperature and concentration based on experimental observations. The mean flow equations are then integrated over the whole plume cross-section to produce ordinary differential equations. The entrainment rate is also assumed, usually as a function of the local centreline velocity.
Theoretical analysis of self-similar plumes using integral methods began more than 50 years ago with the works of Yih [12], Rouse et al [13], Batchelor [14] and Morton et al [15] for plumes with small density differences in unstratified and stratified environments. More recently, these theories have been extended to consider plumes with significant density differences [16][17], with unsteady source strengths [18][19][20] and fire plumes [21][22] [23][24].
The simplest analysis proceeds by assuming that the velocity and buoyancy force are constant across the plume and zero outside it (i.e. a 'top hat' profile). Transport equations for the conservation of volume, momentum and density deficit are integrated analytically with respect to the vertical distance, x, to arrive at expressions for the plume radius, b, the vertical velocity, U, and the density, ρ, inside the plume
where ρ1 is a reference density, α is an empirical entrainment coefficient and Q is the buoyancy flux, given by:
The empirical entrainment coefficient, α, relates the entrainment velocity, Ue, to the plume velocity (Ue = αU). This analysis was first published by Schmidt
[25] and is described in Morton et al [15].
Morton et al [15] extended the above approach, assuming Gaussian radial profiles for the velocity and buoyancy force instead of top-hat profiles. They found that the spreading rate of the plume (db/dx) was equal to 6α/5 and was independent of the strength of the buoyancy source. In their analysis they defined the plume radius, b, as the point where the velocity fell to e-1 of its centreline value (0.37Uc). Experiments undertaken by Morton et al. [15] of positively buoyant plumes in stratified saline solutions found the entrainment coefficient to be around α = 0.093. More recent studies have suggested a value of α ≈ 0.082 for plumes in unstratified environments (for comparison, the entrainment constant for pure jets is α ≈ 0.057) [4][26].
Recently, Diez & Dahm [27] developed an alternative integral approach that does not rely upon the entrainment coefficient, α. Instead, it uses the integral equation for the momentum flux to develop an equation for the local centreline velocity. Diez & Dahm's model relies upon a parameter, cδ, which experiments show to be constant in the far-field of both jets and plumes.
Further details of integral methods applied to plumes and jets, including discussion of empirical models for α as a function of the Froude number, can be found in Chen & Rodi [1] and Gebhart et al [4].
Whilst integral methods can provide accurate results for relatively simple plumes it is difficult to extend the approach to model more complex turbulent flows, where for example the plume may hit a wall or encounter regions of flow recirculation. To study these more complex flows, a more general-purpose CFD approach must be used.
Review of UFR studies and choice of test case
CFD simulations of fully-developed, self-similar turbulent buoyant plumes have, to date, mainly solved the Reynolds-Averaged Navier Stokes (RANS) equations. Whilst Large Eddy Simulation (LES) can in theory be used to study such flows, it involves significantly greater computing resources. To the author's knowledge, the only study of the far-field, self-similar behaviour of plumes using LES is that undertaken by Zhou et al. [28][29]. They simulated the thermal plumes of George et al. [3] and Shabbir & George [11] in [28] and those of Cetegen [30] in [29]. Whilst axisymmetric RANS simulations of these flows would involve meshes with around 4,000 cells, the large-eddy simulations of Zhou et al. [28][29] used more than 4 million cells.
Before describing the experimental and CFD studies on which this UFR documentation will be based, a brief review is provided below of other studies of the axisymmetric buoyant plume which, for various reasons, have not been adopted here.
Review of the nearly-relevant work
Experiments
There have been numerous experimental studies of the turbulent buoyant plume. A major review was undertaken by Chen & Rodi in 1980 [1]. They provided recommended values for the spreading rates of the plume based on the momentum and temperature or concentration of and . The momentum value was based on the experiments of George et al. [3] which were considered to be the most consistent of the reviewed data.
Following Chen & Rodi's review, in the late 1980's and early 90's, Shabbir, George and Taulbee at the University of Buffalo published a number of papers on buoyant plume experiments
[31][32]
[33][34].
In [33] they compared the magnitude of various terms in the k – ε model equations to values obtained directly from experiments. A particularly significant finding was that the streamwise heat flux, , was underpredicted by a factor of four using the standard k – ε model with the Simple Gradient Diffusion Hypothesis (SGDH) (described later). Apart from this shortcoming, however, the k – ε model was found to perform reasonably well.
More recently, Dai et al. [10] performed experiments using negatively-buoyant plumes of CO2 and SF6 in air. A summary table, comparing their results for the axisymmetric buoyant plume against those of Papantoniou & List [35],
Papanicolaou & List [9][36],
Shabbir & George [34]
and George et al. [3] is reproduced in Table 1a.
| Source | Fr0 | |
| Dai et al. [10] | 3.75, 7.80 | |
| Papantoniou and List (1989) | 1.89, 2.24 | |
| Papanicolaou and List (1988) | 0.87 to 3.88 | |
| Papanicolaou and List (1987) | 0.41 to 7.79 | |
| Shabbir and George (1992) | 1.60, 1.80 | |
| George et al. (1977) | 1.23 | |
The third and fourth columns of Table 1a define the extent of the fully-developed flow regions in the axial
direction made dimensionless using the source diameter, d, and the Morton length scale, lM..
Dai et al. [10][37]
[38][39],
suggested that the large range in values of (x - x0)/lM
shown in Table 1a is due to the fact that many researchers had incorrectly made measurements of transitional
plumes exhibiting quasi-jet-like behaviour, rather than fully-developed, self-similar plumes. They attributed
this partly to the difficulty in measuring concentrations accurately at significant distances from the source
due to the relatively fast (x – x0)-5/3 decay rate of scalars in plumes. They
also noted that flow velocities in plumes are relatively low compared to jets, and so greater care had to be
taken in the far field to prevent small external disturbances affecting measurements.
This matter was disputed by Shabbir & George [11]
and George [40]
who noted that plume measurements
are strongly influenced by ambient thermal stratification. Since stratification is more difficult to control
the further ones goes from the source, this could potentially affect measurements taken at larger axial
distances, such as those taken by
Dai et al. [10][37]
[38][39]
at distances of z/D up to 151. In a neutral environment,
conservation of energy implies conservation of buoyancy [1].
One means to check whether ambient thermal
stratification has adversely affected measurements is therefore to ensure that buoyancy is conserved.
Shabbir & George [11]
carefully determined the rate of buoyancy added at the source and found that in their
measurements, buoyancy was conserved to within 10%.
The other columns in Table 1a provide details of the shape of the self-similar profiles of the scalar
within the fully-developed region.
The radial mean scalar profiles were approximated using a Gaussian profile:
To obtain self-similar profiles, the mean properties were then scaled using the following formula,
from List [6]:
The final two columns in Table 1a provide centreline values of the dimensionless
mean scalar, F(0), and RMS scalar fluctuations,
,
for the various
experiments. The sixth column provides details of the spreading rate of the plume, denoted
, where is the plume radius as defined by the point
where falls to e-1 of its centreline value.
The experiments undertaken by
Dai et al. [10][37]
[38][39]
indicated that self-similar round turbulent plumes were up to 40% narrower and had mean
centreline scalar values and streamwise velocities that were up to 30% larger than were previously thought.
This finding was confirmed by a later study by the same group using the same
experimental arrangements [41].
The paper by Brescianini & Delichatsios [10] provides cross-plots of both Dai et al. [10] and
George et al [3] velocity profiles.
These show that on a graph of velocity, U, versus radial location
r/(x – x0), the experimental profile from
George et al. [10] is significantly
flatter and wider than the more recent data of
Dai et al. [10]. However, when plotted in dimensionless
form (U/Uc versus r/r1/2) the data are remarkably similar.
In 1994, Shabbir & George [11]
repeated the earlier experiments of
George et al. [3] with the joint
aim of reproducing the earlier experiments under stricter laboratory conditions and investigating the budgets
of the mean energy and momentum equations. The peak mean values and plume half-widths were found to be in good
agreement with their earlier work
(see also Heskestad [43] for comparisons).
Shabbir & Taulbee [44] recently provided further analysis
of the budgets for the turbulent heat flux and Reynolds stress
transport equations to help with the development
of new second-moment closure models. They found that the “local equilibrium assumption”
(where production and dissipation are in balance) provided a reasonable approximation for the turbulent heat flux transport equation
but that convection and diffusion terms were significant in the Reynolds stress budgets. This finding has
implications for the development of algebraic stress models (see later). A priori assessment of simple
pressure-correlation models for the turbulent heat flux and Reynolds stress equations were also presented in
[44].
They found that the measured axial heat flux,
,
was generally
several times larger than that modelled by a simple Boussinesq gradient diffusion form and proposed an
algebraic stress model to improve its prediction.
A recent experimental study by Yao & Marshall [45]
used Planar Laser Induced Fluorescence (PLIF) to investigate turbulent buoyant salt-water plumes.
Results were given for the fully-developed region extending approximately from 6 < (x-x0)/D < 30,
where the mean plume radius was found to increase linearly and the dimensionless
density difference decay according to the -5/3 law. Velocity measurements were not made. Dimensionless RMS
concentration fluctuations varied between 0.35 and 0.45, in fair agreement with the earlier experiments
reported in Table 1a. The purpose of Yao & Marshall's measurements was to simulate fire plumes. However, as
they noted, care should be taken in interpreting data from salt-water experiments since the Schmidt number in
liquid plumes is nearly three orders of magnitude larger than the corresponding value in gaseous plumes. The
effect of this higher Schmidt number is to inhibit scalar mixing at small scales and near walls, where
molecular diffusion is significant.
The review paper by Heskestad [43],
discussed briefly the variability in reported measured peak values and
spreading rates in axisymmetric plume experiments, shown in Table 2. Heskestad's earlier
fire plume measurements [22],
were in reasonably good agreement with the measurements of
George et al. [3].
For the spreading rate of the plume, Heskestad [heske98] commented
that the
George et al. [3]
and Shabbir & George [11]
experiments were considered the most reliable.
Chen & Rodi [1]
also considered the work of
George et al. [3]
to be the most consistent of their reviewed data.
| Study | Centreline velocity, U0 | Half-width based on velocity, bU | Centreline temperature difference, ΔT0 | Half-width based on temperature, bΔT |
| Hesketad [22] | 3.4 | — | 9.1 | 0.12 |
| George et al. [3] | 3.4 | 1.08 | 9.1 | 0.104 |
| Shabbir & George [11] | 3.4 | 1.07 | 9.4 | 0.10 |
| Papanicolaou & List [9] | 3.9 | — | 14.3 | 0.09 |
| Dai et al. [10] | — | — | 12.6 | 0.08 |
CFD Studies
One of the most comprehensive early CFD studies of buoyant plumes was undertaken by Hossain & Rodi [8]. They examined the performance of an algebraic stress and heat flux model in axisymmetric and plane plumes, buoyant jets and pure jets. Their model was based on the differential stress model of Gibson & Launder [46] which is described in some detail in their paper. They showed how the differential model was simplified to algebraic expressions by neglecting the convective and diffusive fluxes, effectively assuming that the flow only evolves slowly (i.e. local equilibrium). The validity of this assumption in buoyant plumes was examined subsequently by Shabbir & Taulbee [33]. The proposed algebraic model shared some features with the standard k – ε model but used modified expressions for the stresses and heat fluxes and a more sophisticated diffusion term. An important feature of the model was that the coefficients appearing in the eddy viscosity and diffusivity were functions of buoyancy parameters (not the case with the standard k – ε model). The model also incorporated an empirical correction for the round-jet/plane-jet anomaly first proposed by Rodi [47]. The buoyancy term in the modelled ε-equation was empirical in nature and Hossain & Rodi [8] acknowledged that it would not be well suited to more general flow situations. To simulate the axisymmetric plume, they used a parabolic method where the numerical grid adjusted itself to the increase in plume width using a dimensionless stream function as a lateral coordinate. Both the limiting cases of pure jets and pure plumes were well predicted by the algebraic model as was the transition between jet and plume-behaviour in buoyant jets.
A number of more recent CFD simulations of axisymmetric buoyant plumes have also used variants of the
standard k – ε turbulence model.
Nam & Bill [48]
performed simulations of pool fires using the commercial
code PHOENICS and modified the standard
Launder & Spalding [49]
model by changing, arbitrarily, the values of
the effective Prandtl number, σeff, and the model constant, cμ, from 1.0
and 0.09 to 0.614 and 0.109, respectively, to obtain improved results in buoyant plumes. They then used their
modified model to simulate buoyant ceiling jets and found results to be slightly better than with the standard
model. The consequences of changing these constants on the model's performance in other flows was not explored.
Hara & Kato [50]
used a standard k – ε model and presented results using different meshes with
various modifications to the cε3 constant in the buoyancy production term of the
ε-equation. They compared results to the experiments of
Yokoi [51],
which involved releases of buoyant
fluid through a circular orifice, but modelled this as a square orifice to enable the use of hexahedral
Cartesian grids. Results were found to be grid-sensitive and recommendations regarding resolution were
provided. Differences in the cε3 constant were found to have no effect on results.
The study by Brescianini & Delichatsios [42]
also examined the k – ε model in combination with different
sub-models for the turbulence production due to buoyancy, including the Boussinesq Simple Gradient Diffusion
Hypothesis (SGDH), the Generalized Gradient Diffusion Hypothesis (GGDH) of
Daly & Harlow [52] and the
algebraic model of Hossain & Rodi [8].
The SGDH and GGDH models are described in detail later in this
UFR. They compared CFD predictions mainly to the experimental measurements of
Dai et al. [41] and
examined both axisymmetric and plane plumes. None of the model variants were found to capture all the flow
details of both axisymmetric and plane plumes and no firm conclusions were drawn regarding the best turbulence
buoyancy production model. The GGDH model was found to give improved predictions of the streamwise mass flux
compared to SGDH.
The Hossain & Rodi [8]
model was also found sometimes to produce better results than
GGDH. However, Brescianini & Delichatsios [42]
noted that the Hossain & Rodi [8]
model was sensitive
to the model constants and was more complex to implement. They concluded that given the overall satisfactory
performance of the k – ε model in predicting the mean-flow quantities, there was no real advantage to be
gained in using a higher-order closure model to study buoyant plumes.
Yan & Holmstedt [53]
compared two k – ε model variants against the
George et al. [3]
experiments for the axisymmetric plume. The first variant was a standard k – ε model with SGDH and the
second involved an additional algebraic stress model for the production term in the k-equation combined
with GGDH for the production due to buoyancy. The additional algebraic stress model was based on a
second-moment-closure correction devised by
Davidson [54]
The k – ε model with SGDH was found to underpredict the spreading rate of the plume, producing overly-high
temperatures and velocities in the core. Their modified model produced better results for the axisymmetric
plume. They went on to examine buoyant diffusion flames using their new approach.
Malin & Younis [55]
also compared CFD predictions to the George et al. [3]
data but used second-moment-closure models and the parabolic PHOENICS solver. The objective of Malin & Younis's
study was to extend the second-moment closure model of
Gibson & Younis
[56][57][58] to buoyant flows
and examine its performance in free turbulent jets and plumes. The model produced good predictions of the mean
axial velocity and temperature profiles and was able to capture, at least qualitatively, the anisotropy in the
Reynolds stresses.
Van Maele & Merci [2]
recently examined both an axisymmetric and a plane buoyant wall plume using SGDH and GGDH variants of the
standard k – ε model and a realizable k – ε model with the commercial code, Fluent. The SGDH source
term was shown to have little effect in the axisymmetric plume case, and consequently the turbulent kinetic
energy was underpredicted and the centreline velocity and temperature were overpredicted. The GGDH model was
found to perform well with either of the two k – ε model variants. For the axisymmetric plume case,
results were compared to the experimental data of
George et al. [3].
Finally, Craft et al. [59]
mentioned briefly the results for the buoyant plume in discussing developments of their Two-Component Limit
(TCL) second-moment-closure model. Predictions using the TCL model were compared to the experiments of
Cresswell et al. [60]
and results from a “basic” second-moment-closure model. The spreading rate of the self-similar buoyant plume
was found to be better predicted using the more sophisticated TCL model.
Parabolic Solvers
A number of the early CFD studies discussed above used a parabolic or space-marching solution method. This involves the solution of simplified boundary-layer-type transport equations. Comparisons of model predictions using parabolic and elliptic codes for jets and plumes are given by El Baz et al. [61], Magi et al. [62] and Haroutunian & Launder [63]. In axisymmetric free-jets, El Baz et al. [61] and Magi et al. [62] found that the use of an elliptic instead of a parabolic approach resulted in differences in the predicted spreading rates of 10% or more. In axisymmetric buoyant plumes, Haroutunian & Launder [63] found that spreading rates differed by only a few percent, but second moments differed by more than 30% in some cases. Given the capabilities of current desktop computers, there is no longer a need on the grounds of grid-resolution and computing time to use a parabolic solver in far-field plume simulations. However, care must be taken when using elliptic codes to ensure that the solution is not restricted or influenced by the side entrainment boundaries.
Studies on which this UFR review will be based
The work of Van Maele & Merci [2] has been chosen as providing the most appropriate currently available information on which comparisons have been made between CFD and experiment. Their study represents a good match for what is required for this UFR. They examined SGDH and GGDH variants of the both the standard k – ε model and a realizable k – ε model using the commercial CFD software, Fluent. The paper provides a thorough description of methodology used, including description of the numerical methods and a grid-dependence study. Both axisymmetric and plane wall plumes were examined, the former using the experimental data of George et al. [3]. The methodology used in their studies is described below.
Footnotes
- ↑ In some cases, the densimetric Froude number is defined with the density difference made dimensionless using the plume source density, ρ, instead of the ambient density ρ∞, e.g. Chen & Rodi [1] and Hossain & Rodi [8].
- ↑ The local Froude number in this case is evaluated on the plume centreline. Note, the Fr defined by Chen & Rodi [1] is the square of the definition of Fr given above.
Contributed by: Simon Gant — UK Health & Safety Laboratory
© copyright ERCOFTAC 2010
![{\displaystyle {Fr}={\frac {U}{\sqrt {\left[gD\left({\frac {\rho _{\infty }-\rho }{\rho _{\infty }}}\right)\right]}}}}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/eda46d727d338b7aefdfb3c743d86df32b4540de)


























![{\displaystyle F\left({\frac {r}{x-x_{0}}}\right)=F(0)\exp \left[-k_{f}^{2}\left({\frac {r}{x-x_{0}}}\right)^{2}\right]}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a11490a839704407ffcf0d8a546fedda06772e3c)






